|
Traditional Tibetan medicine
Traditional Tibetan medicine introduction[Top] Tibetan medicine is practiced in Bhutan, Mongolia, China, Siberia, Ladakh, and in North America and many countries in Europe where it continues to grow in popularity. Ayurvedic medicine in particular has had a big influence on traditional Tibetan medicine. Ayurvedic medical books such as the Astanga hrdya of Vagbhata, Susruta and Charaka strong influenced important Tibetan medical texts such as the four great tantras and the four treatises which forms a great deal of the Tibetan source book.
Therapies in Tibetan medicine[Top] Herbal medicine is a large part of Tibetan medicine, see Tibetan herbal medicine in addition to this minerals, animal extract, salts and stones both semiprecious and precious are also used. In fact in Tibetan medicine all the substances on earth have medicinal value. Other therapies include massage, cold and hot fomentation, enemas and purging, moxabustion, cupping, meditation and medicine bath.
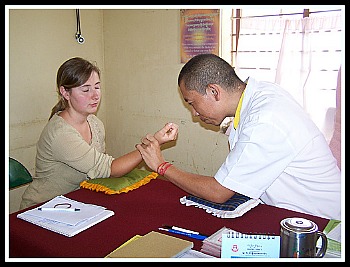
Diagnostic methods in Tibetan medicine[Top] The Tibetan diagnostic method of diseases includes analyzing the urine and the pulse. For doctors in conventional medicine, pulse examination, simply involves feeling the pulse of a patient's wrist. For Tibetan doctors this is the not case, to correctly examine pulses in Tibetan medicine, extensive theoretical study is needed followed by some years of practical experience. This is also the case with urine analysis; it takes years of experience and training to do it correctly. See the video below
The spread of Tibetan medicine in China[Top] Traditional Tibetan medicine started to become popular in China when Lochen Rinchen Sangpo's medical text called sman dpyad yan lag brgyad pa'i snying po bsdus pa (Astanga Hrdaya Samhita) during Pal Phakmo Grub pa time was published and translated in Chinese. There are now more than twenty kinds of Tibetan medicines in China's pharmacopoeia. 336 types of Tibetan medicines are produced to ministerial-level standards. There are more than three hundred hospitals using thirty five kinds of Tibetan medicines and fifty seven Tibetan medicine hospitals.
Return to traditional Chinese medicine
Return to natural healing home
|
Loading